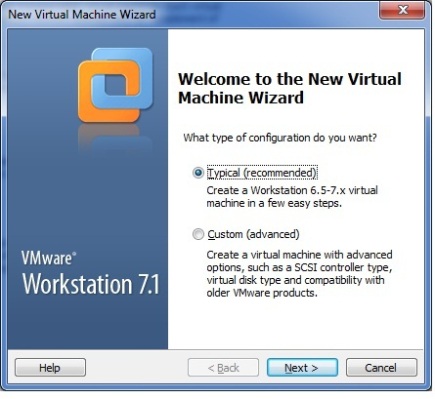
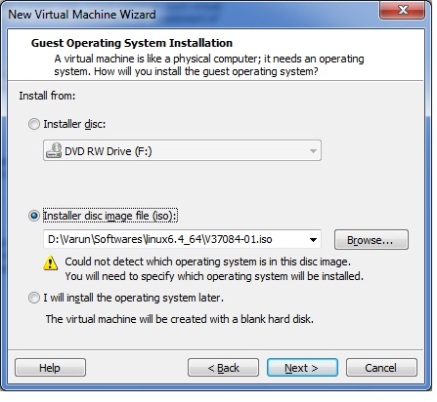
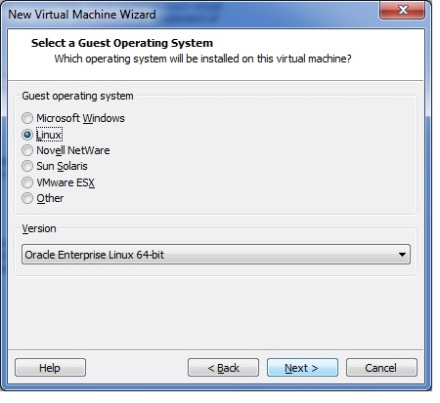
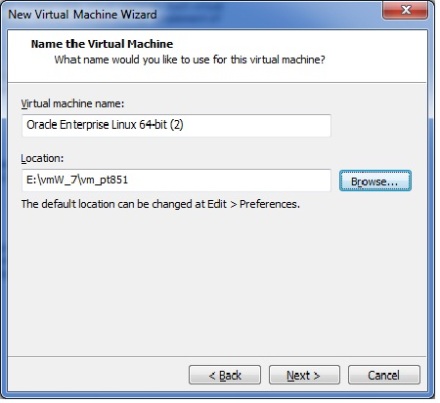
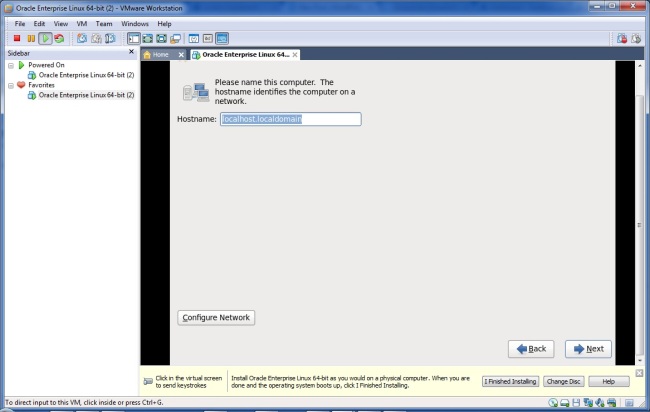
1. Below command counts X days old files and directories at Present directory.If you want to sort from different directory use path instead of dot(.)
find . -mtime +x | wc -l (present directory)
find /home/varun/ -mtime +x | wc -l (sort in different directory)
2.Below Command lists X days old files and directories.
find . -mtime +x | ls -ltr
3.Below command lists specific format files of X days old.
example: If you want all files which are 50 days older and end with log extension
find -name “*.log” –mtime +50
4.If you want to delete 50 days old files with extension “.log”.
find . -name “*.log” -mtime +50 -exec rm -f {} \;
5.If you want to delete 50(any number) days old files and directories recursively then use below command.
find . -mtime +1100 -exec rm -rf {} \;
More Info:
find: the command that will search for the files
/path/to/files/: the top level directory to start searching
-type f: so we don’t remove directories, only files
-mtime +7: files older than ’7′ days. Change to ‘+14′ to delete files older than 2 weeks.
-exec: what to do with the files we find
rm -rf: remove them recursively, force
{}: this represents each file we find
\;: the end of the exec